Objective 🎯
Provide a way to interpret/evaluate a language grammar or expression.
Type ✅
✔️Behavioral: Describes how objects interact/communicate between themselves.
❌Creational: Describes how to instantiate an object without large and complex.
❌Structural: Describes how objects/classes are composed to form larger structures.
UML 📐
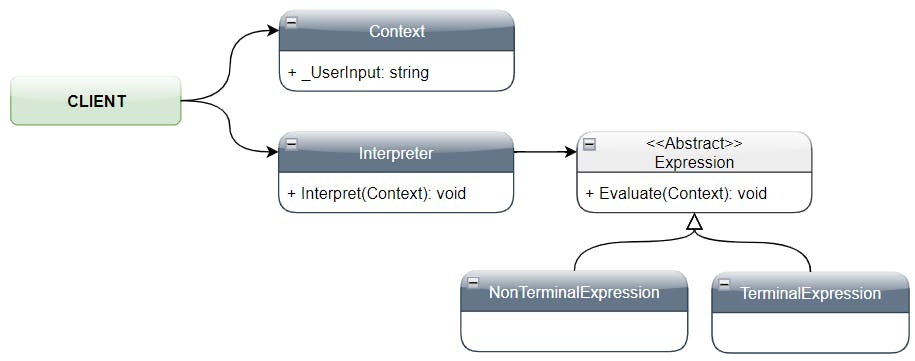
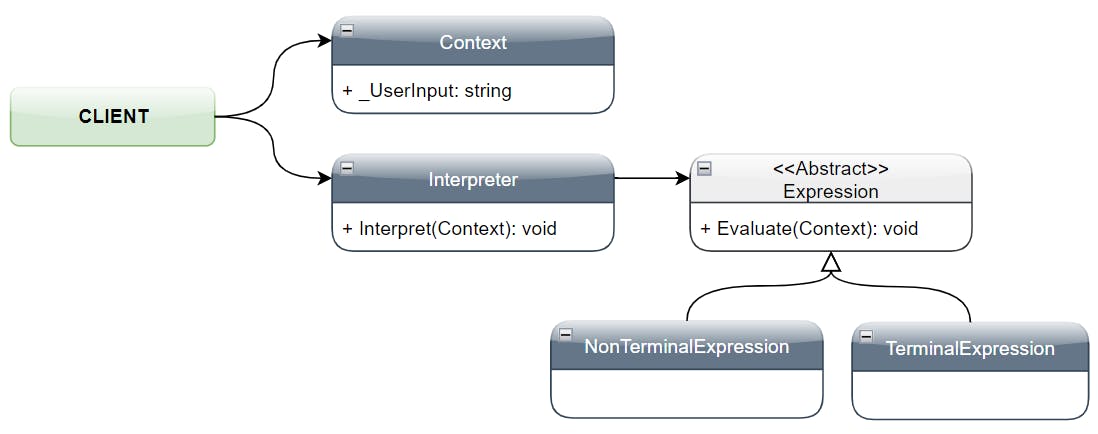
Participants 🔗
• AbstractExpression:
- Declares an Evaluate() operation that all nodes (leaf and non-leaf) must override
• Terminal Expression:
- Implements a concrete operation
• Nonterminal Expression:
- Implements an operation and execute the next expression
• Interpreter:
- Defines an interface to receive the Context
- Based on the Context (user’s input) will create the Expression classes
- Will interpret the user’s input (Context) by executing the Evaluate method of the Expression classes
• Client:
- Will receive the user’s input data
- Responsible to create and maintain the Context
- Will instantiate an Interpreter object and call the method Interpret passing the Context as argument
Notes 📝
• This pattern is recommended for relatively simple grammar interpretation, which doesn't need to evolve and extend much.
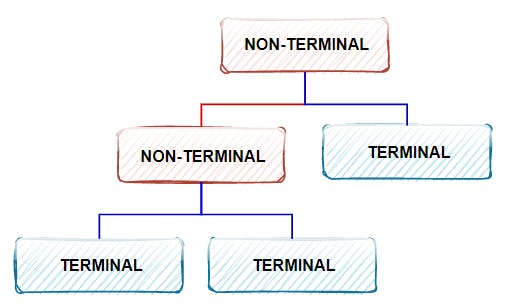
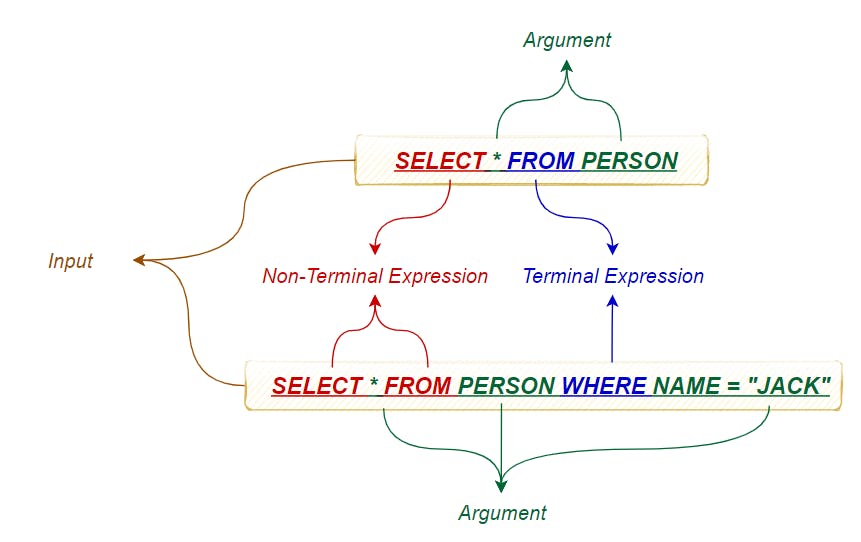
• Terminal Expressions are considered the leaf nodes
• Non-Terminal Expressions are considered the non-leaf nodes
• The example below illustrates how this pattern can be used to interpret SQL statements
Sample Code 🎮
Structural Example 🏛️
public static class InterpreterStructural
{
// Client
public static void Execute()
{
Context lContext = new Context();
lContext._UserInput = "AABBCC";
Interpreter lInterpreter = new Interpreter();
lInterpreter.Interprete(lContext);
}
}
public class Interpreter
{
public void Interprete(Context prContext)
{
List<Expression> _Expressions = new List<Expression>();
_Expressions.Add(new NonTerminalExpression());
_Expressions.Add(new TerminalExpression());
foreach (Expression lExpressionCurrent in _Expressions)
{
lExpressionCurrent.Evaluate(prContext);
}
}
}
public abstract class Expression
{
public abstract void Evaluate(Context prContext);
}
public class NonTerminalExpression : Expression
{
public override void Evaluate(Context prContext)
{
Console.WriteLine($"--Executing a Non-Terminal Operation with the input \"{prContext._UserInput}\"");
}
}
public class TerminalExpression : Expression
{
public override void Evaluate(Context prContext)
{
Console.WriteLine($"----Executing a Terminal Operation with the input \"{prContext._UserInput}\"");
}
}
public class Context
{
public string _UserInput { get; set; }
}
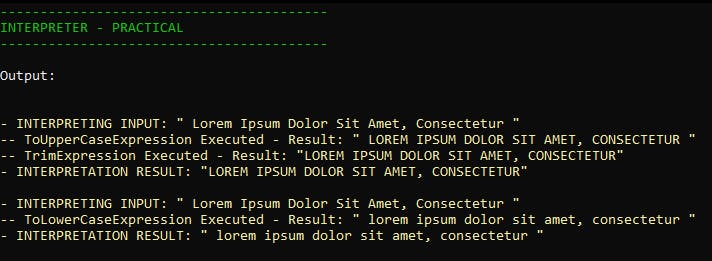
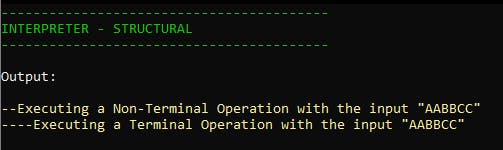
Output
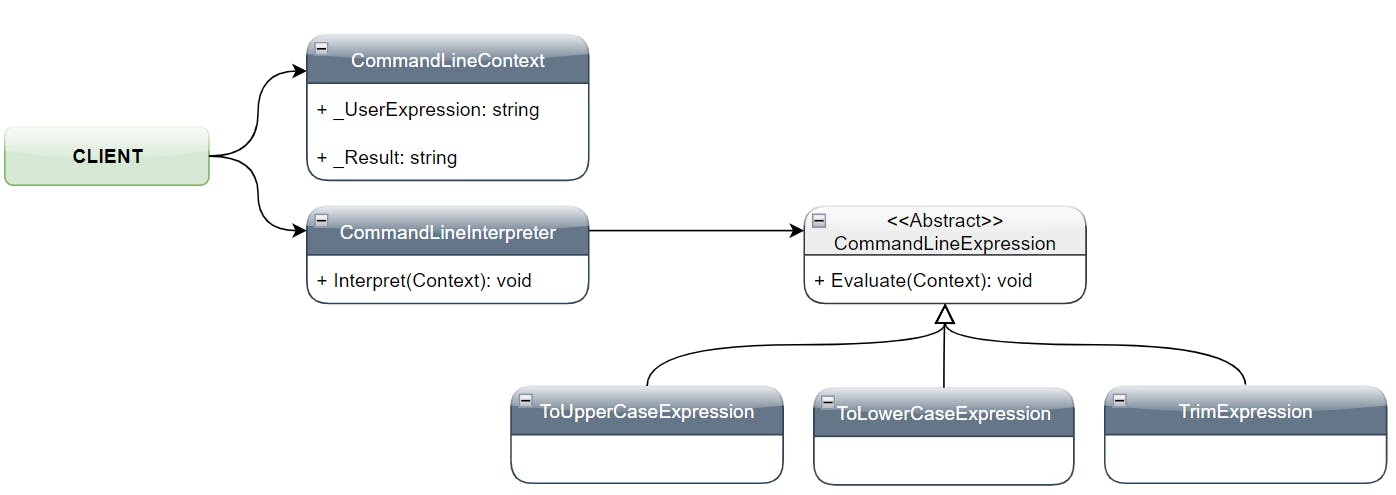
Real-world Example 🔥
public static class InterpreterPractical
{
// Client
public static void Execute()
{
CommandLineContext lCommandLineContext = new CommandLineContext();
lCommandLineContext._UserExpression = " Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet, Consectetur -u -t";
CommandLineInterpreter lCommandLineInterpreter = new CommandLineInterpreter();
lCommandLineInterpreter.Interprete(lCommandLineContext);
lCommandLineContext._UserExpression = " Lorem Ipsum Dolor Sit Amet, Consectetur -l";
lCommandLineInterpreter.Interprete(lCommandLineContext);
}
}
public class CommandLineInterpreter
{
public void Interprete(CommandLineContext prCommandLineContext)
{
List<CommandLineExpression> _CommandLineExpressions = new List<CommandLineExpression>();
// GET EXPRESSIONS
List<string> lExpressions = prCommandLineContext._UserExpression.Substring(prCommandLineContext._UserExpression.IndexOf("-")).Split(" ").ToList();
prCommandLineContext._Result = prCommandLineContext._UserExpression.Substring(0, prCommandLineContext._UserExpression.IndexOf("-"));
foreach (string lExpressionCUrrent in lExpressions)
{
switch (lExpressionCUrrent)
{
case ("-u"): _CommandLineExpressions.Add(new ToUpperCaseExpression()); break;
case ("-l"): _CommandLineExpressions.Add(new ToLowerCaseExpression()); break;
case ("-t"): _CommandLineExpressions.Add(new TrimExpression()); break;
default: break;
}
}
// EXECUTE EXPRESSIONS
Console.WriteLine($"\n\r- INTERPRETING INPUT: \"{prCommandLineContext._Result}\"");
foreach (CommandLineExpression lCommandLineExpressionCurrent in _CommandLineExpressions)
{
lCommandLineExpressionCurrent.Evaluate(prCommandLineContext);
Console.WriteLine($"-- {lCommandLineExpressionCurrent.GetType().Name} Executed - Result: \"{prCommandLineContext._Result}\"");
}
Console.WriteLine($"- INTERPRETATION RESULT: \"{prCommandLineContext._Result}\"");
}
}
public abstract class CommandLineExpression
{
public abstract void Evaluate(CommandLineContext prCommandLineContext);
}
public class ToUpperCaseExpression : CommandLineExpression
{
public override void Evaluate(CommandLineContext prCommandLineContext)
{
prCommandLineContext._Result = prCommandLineContext._Result.ToUpper();
}
}
public class ToLowerCaseExpression : CommandLineExpression
{
public override void Evaluate(CommandLineContext prCommandLineContext)
{
prCommandLineContext._Result = prCommandLineContext._Result.ToLower();
}
}
public class TrimExpression : CommandLineExpression
{
public override void Evaluate(CommandLineContext prCommandLineContext)
{
prCommandLineContext._Result = prCommandLineContext._Result.Trim();
}
}
public class CommandLineContext
{
public string _UserExpression { get; set; }
public string _Result { get; set; }
}
Output